목차
Design Pattern
25.01.02
: Design Pattern을 공부할 때는 왜 쓰는지? 어떤 목적으로 쓰는지? 그 맥락을 아는 것이 중요하다.
초기 세팅
>> 새 프로젝트 생성

>> Unity Chan 추가

>> 깨지는 Material을 바로잡기 위해 Toon Shader 추가
- package manager에서 toon shader 추가


>> Plane의 Material을 Toon으로 변경

>> UnityChan의 Material을 Toon으로 변경

>> 홍조 세부 조정

>> UnityChan Prefab을 복사하여 Transform과 Animator만 남기고 전부 삭제

>> Animator Controller 생성 후 세팅
- Blend Tree 생성

- Parameter 이름 변경 및 Motion Field 추가

- Jump Motion 추가

- MyChan Prefab에 만든 Animator Controller 세팅

>> Input System 추가
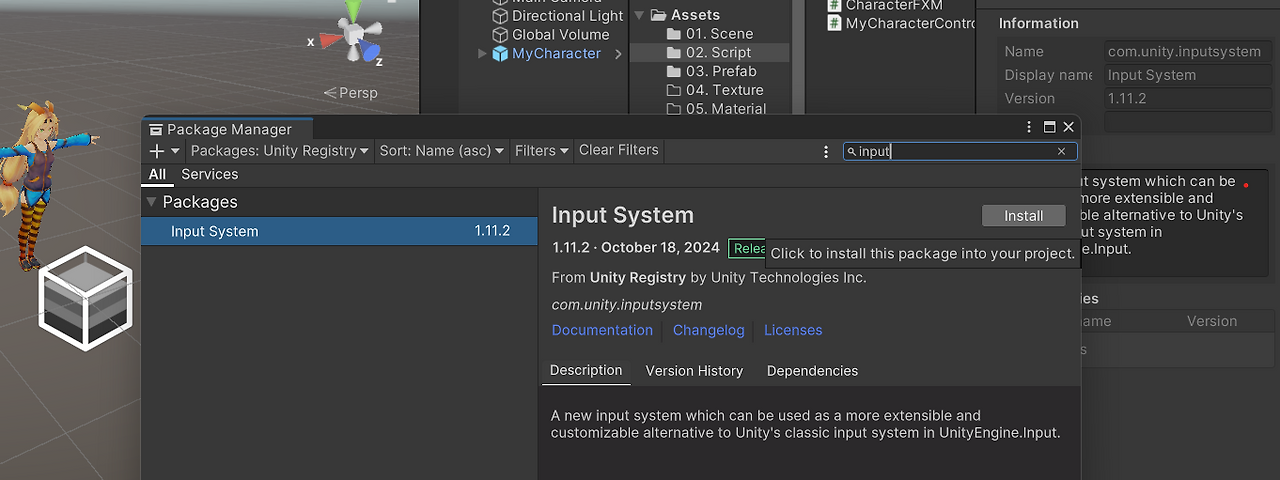
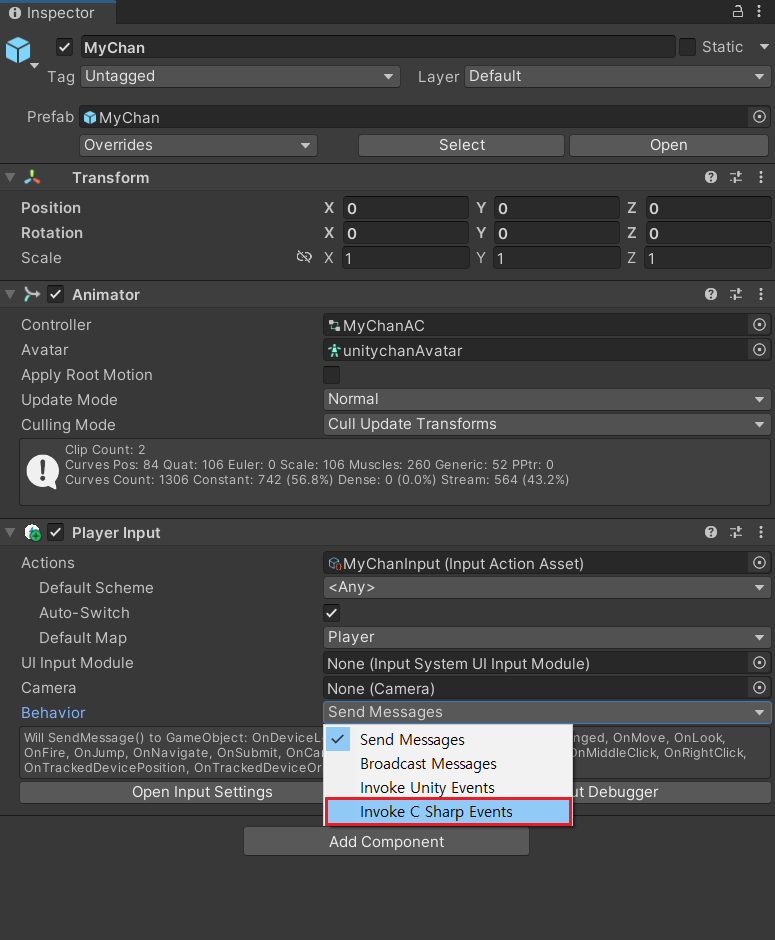
- MyChan에 Player Input을 추가한 뒤, Action 생성

- Actions에 Jump 추가

- Behavior 설정
>> Rigidbody, Capsule Collider 추가 및 세부 설정

FSM Pattern (enum)
: CharacterFSM.cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.InputSystem;
public enum CharacterFSMState
{
Idle,
Walk,
Jump
}
public class CharacterFSM : MonoBehaviour // 캐릭터 상태를 관리
{
// 문자열을 int로 바꿔서 캐싱하기 때문에 성능적으로 훨씬 좋아진다.
private static readonly int Speed_Hash = Animator.StringToHash("Speed");
private CharacterFSMState currentState = CharacterFSMState.Idle;
private CharacterFSMState prevState = CharacterFSMState.Idle;
private Rigidbody rb;
[SerializeField] private float moveSpeed = 3.0f;
[SerializeField] private float jumpForce = 5.0f;
private bool isGrounded;
private Vector2 moveInput;
private InputAction moveAction;
private InputAction jumpAction;
private Animator animator;
void Start()
{
rb = GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
animator = GetComponent<Animator>();
currentState = CharacterFSMState.Idle; // 혹시 다른 곳에서 건드릴 수 있으니 한번 더 선언
moveAction = GetComponent<PlayerInput>().actions["Move"];
jumpAction = GetComponent<PlayerInput>().actions["Jump"];
}
void Update()
{
// 움직임 값 확인
moveInput = moveAction.ReadValue<Vector2>();
bool bPressedJump = jumpAction.triggered;
// 점프 상태 확인
GroundCheck();
StateChange(bPressedJump);
EnterState();
UpdateState();
ExitState();
}
private void GroundCheck()
{
isGrounded = rb.velocity.y == 0.0f;
}
private void StateChange(bool bPressedJump)
{
prevState = currentState;
switch (currentState)
{
case CharacterFSMState.Idle:
{
// sqrMagnitude : 제곱근이 되기 전의 Magnitude
if (moveInput.sqrMagnitude > 0.0f)
{
currentState = CharacterFSMState.Walk;
}
if (bPressedJump && isGrounded)
currentState = CharacterFSMState.Jump;
}
break;
case CharacterFSMState.Walk:
{
if (moveInput.sqrMagnitude <= 0.0f)
{
currentState = CharacterFSMState.Idle;
}
if (bPressedJump && isGrounded)
currentState = CharacterFSMState.Jump;
}
break;
case CharacterFSMState.Jump:
{
if (isGrounded)
{
currentState = CharacterFSMState.Idle;
}
}
break;
}
}
private void EnterState()
{
if (prevState != currentState)
{
switch (currentState)
{
case CharacterFSMState.Idle:
{
animator.SetFloat(Speed_Hash, 0.0f);
}
break;
case CharacterFSMState.Walk:
{
animator.SetFloat(Speed_Hash, 1.0f);
}
break;
case CharacterFSMState.Jump:
{
animator.CrossFade("Jump", 0.1f);
rb.velocity = new Vector3(moveInput.x * moveSpeed, jumpForce, rb.velocity.z);
}
break;
}
}
}
private void UpdateState()
{
switch (currentState)
{
case CharacterFSMState.Idle:
break;
case CharacterFSMState.Walk:
rb.velocity = new Vector3(moveInput.x * moveSpeed, rb.velocity.y, moveInput.y * moveSpeed);
// y값으로 rb.velocity를 넣은 것은 y값이 그대로 유지되도록 하기 위해 --> 0으로 넣으면 무중력이 되어버림
// 벡터는 방향을 가진 힘이기 때문에 그대로 넣어줘야 함
break;
case CharacterFSMState.Jump:
break;
}
}
private void ExitState()
{
if (prevState != currentState)
{
switch (prevState)
{
case CharacterFSMState.Jump:
{
animator.CrossFade("Idles", 0.1f);
}
break;
}
}
}
}FSM Pattern (Interface)
: 코드가 Class 단위로 분산되는 장점이 있다. 즉, 다양한 행동 패턴이 있고 복잡할수록 가독성과 확장성이 좋다.
※ State가 늘어날수록 이 방식이 차용된다. --> State가 적다면 enum 방식으로 하는 게 더 나을수도 있다.
Idle, Walk, Jump를 각각 Script로 나누고 Interface인 IState.cs와 StateMachine.cs와 MyCharacterFSM_I.cs 추가
>> IState.cs
public interface IState
{
StateMachine Fsm { get; set; }
void InitState();
void Enter();
void UpdateState(float deltaTime);
void Exit();
}
>> StateMachine.cs
: State 관리와 전환 담당
※ 상태 전환 과정
- 이전 상태의 Exit을 호출하여 이전 상태 종료
- 상태 전환
- 새로운 상태의 Enter를 호출
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class StateMachine : MonoBehaviour // State 관리와 전환 담당
{
[SerializeField]private string defaultState;
private IState currentState;
private Dictionary<Type, IState> stateDict = new();
public void Run()
{
IState[] states = GetComponents<IState>();
foreach (var state in states)
{
AddState(state);
}
ChangeState(Type.GetType(defaultState));
}
public void AddState(IState state)
{
state.Fsm = this;
state.InitState();
stateDict.Add(state.GetType(), state);
}
public void ChangeState<T>() where T : IState
{
ChangeState(typeof(T));
}
public void ChangeState(Type stateType)
{
currentState?.Exit(); // 이전 상태의 Exit을 호출하여 이전 상태 종료
if (!stateDict.TryGetValue(stateType, out currentState)) return; // 상태 전환
currentState?.Enter(); // 새로운 상태의 Enter를 호출
}
public void UpdateState() // 현재 상태 업데이트
{
if (currentState != null)
currentState.UpdateState(Time.deltaTime);
}
}currentState?.Exit();※ ? : 이 함수에 접근할 때, currentState가 null이면 실행하지 않고 넘어감
if (!stateDict.TryGetValue(stateType, out currentState)) return;※ TryGetValue : stateType이라는 Key값이 없으면 false를 반환하고, 있으면 currentState에 넣어준다.
--> 따라서 Key값이 없으면 '!' 연산자에 의해 true가 되어 if문으로 들어가고, return을 통해 함수를 중단시킨다.
>> MyCharacterFSM_I.cs
: 코드 시작 부분
using System.Collections;
using UnityEngine;
public class MyCharacterFSM_I : MonoBehaviour
{
private StateMachine stateMachine;
void Start()
{
stateMachine = GetComponent<StateMachine>();
stateMachine.Run();
}
void Update()
{
stateMachine.UpdateState();
}
}※ stateMachine을 가진 객체가 수명 주기를 관리하길 원하기 때문에 Update문을 그대로 사용해도 되지만 stateMachine.UpdateState()를 사용함
>> IdleState.cs 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.InputSystem;
public class IdleState : MonoBehaviour, IState
{
public StateMachine Fsm { get; set; }
private Animator animator;
private Rigidbody rigidbody;
private InputAction moveInput;
private InputAction jumpInput;
public void InitState()
{
animator = Fsm.GetComponent<Animator>();
rigidbody = Fsm.GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
moveInput = Fsm.GetComponent<PlayerInput>().actions["Move"];
jumpInput = Fsm.GetComponent<PlayerInput>().actions["Jump"];
}
public void Enter()
{
animator.CrossFade("Idles", 0.1f);
animator.SetFloat("Speed", 0.0f);
}
public void UpdateState(float deltaTime)
{
if (jumpInput.triggered && rigidbody.velocity.y == 0.0f)
{
Fsm.ChangeState<JumpState>();
return;
}
var value = moveInput.ReadValue<Vector2>();
if (value.sqrMagnitude > 0)
{
Fsm.ChangeState<WalkState>();
}
}
public void Exit()
{
}
}
>> WalkState.cs 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.InputSystem;
public class WalkState : MonoBehaviour, IState
{
[SerializeField] private float moveSpeed = 3.0f;
public StateMachine Fsm { get; set; }
private Animator animator;
private Rigidbody rigidbody;
private InputAction moveInput;
private InputAction jumpInput;
public void InitState()
{
animator = Fsm.GetComponent<Animator>();
rigidbody = Fsm.GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
moveInput = Fsm.GetComponent<PlayerInput>().actions["Move"];
jumpInput = Fsm.GetComponent<PlayerInput>().actions["Jump"];
}
public void Enter()
{
animator.CrossFade("Idles", 0.1f);
animator.SetFloat("Speed", 1.0f);
}
public void UpdateState(float deltaTime)
{
if (jumpInput.triggered && rigidbody.velocity.y == 0.0f)
{
Fsm.ChangeState<JumpState>();
return;
}
var value = moveInput.ReadValue<Vector2>();
if (0 >= value.sqrMagnitude)
{
Fsm.ChangeState<IdleState>();
return;
}
rigidbody.velocity = new Vector3(value.x * moveSpeed, rigidbody.velocity.y, value.y * moveSpeed);
}
public void Exit()
{
}
}
>> JumpState.cs 구현
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class JumpState : MonoBehaviour, IState
{
[SerializeField]private float JumpForce = 3f;
public StateMachine Fsm { get; set; }
private Animator animator;
private Rigidbody rigidbody;
public void InitState()
{
animator = Fsm.GetComponent<Animator>();
rigidbody = Fsm.GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
}
public void Enter()
{
animator.CrossFade("Jump", 0.1f);
rigidbody.velocity = new Vector3(rigidbody.velocity.x, JumpForce, rigidbody.velocity.z);
}
public void UpdateState(float deltaTime)
{
if (rigidbody.velocity.y == 0.0f)
{
Fsm.ChangeState<IdleState>();
}
}
public void Exit()
{
}
}
└ Blackboard 추가
: Interface인 IBlackboardBase.cs 추가, Blackboard_Default.cs 추가 그리고 코드 수정
>> BlackboardBase.cs
public interface IBlackboardBase
{
void InitBlackboard();
}
>> Blackboard_Default.cs
: 공통으로 선언되는 컴포넌트 및 변수들 묶어줌
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.InputSystem;
public class Blackboard_Default : MonoBehaviour, IBlackboardBase
{
public Animator animator;
public Rigidbody rigidbody;
public InputAction moveInput;
public InputAction jumpInput;
public float moveSpeed = 3.0f;
public float jumpForce = 3.0f;
public void InitBlackboard()
{
animator = GetComponent<Animator>();
rigidbody = GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
moveInput = GetComponent<PlayerInput>().actions["Move"];
jumpInput = GetComponent<PlayerInput>().actions["Jump"];
}
}
>> IState.cs
: Blackboard 추가
public interface IState
{
StateMachine Fsm { get; set; }
public Blackboard_Default Blackboard { get; set; }
void InitState(IBlackboardBase blackboard);
void Enter();
void UpdateState(float deltaTime);
void Exit();
}
>> StateMachine.cs
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class StateMachine : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField]private string defaultState;
private IState currentState;
private Dictionary<Type, IState> stateDict = new();
public void Run()
{
IBlackboardBase blackboardBase = GetComponent<IBlackboardBase>();
blackboardBase.InitBlackboard();
IState[] states = GetComponents<IState>();
foreach (var state in states)
{
AddState(state, blackboardBase);
}
ChangeState(Type.GetType(defaultState));
}
public void AddState(IState state, IBlackboardBase blackboard)
{
state.Fsm = this;
state.InitState(blackboard);
stateDict.Add(state.GetType(), state);
}
public void ChangeState<T>() where T : IState
{
ChangeState(typeof(T));
}
public void ChangeState(Type stateType)
{
currentState?.Exit();
if (!stateDict.TryGetValue(stateType, out currentState)) return;
currentState?.Enter();
}
public void UpdateState()
{
if (currentState != null)
currentState.UpdateState(Time.deltaTime);
}
}
>> IdleState.cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.InputSystem;
public class IdleState : MonoBehaviour, IState
{
public StateMachine Fsm { get; set; }
public Blackboard_Default Blackboard { get; set; }
public void InitState(IBlackboardBase blackboard)
{
// as 연산자 : 캐스팅이 가능하면 캐스팅 결과를 반환하고 불가능하면 null을 반환
Blackboard = blackboard as Blackboard_Default;
}
public void Enter()
{
Blackboard.animator.CrossFade("Idles", 0.1f);
Blackboard.animator.SetFloat("Speed", 0.0f);
}
public void UpdateState(float deltaTime)
{
if (Blackboard.jumpInput.triggered && Blackboard.rigidbody.velocity.y == 0.0f)
{
Fsm.ChangeState<JumpState>();
return;
}
var value = Blackboard.moveInput.ReadValue<Vector2>();
if (value.sqrMagnitude > 0)
{
Fsm.ChangeState<WalkState>();
}
}
public void Exit()
{
}
}※ as 연산자 : 캐스팅이 가능하면 캐스팅 결과를 반환하고 불가능하면 null을 반환
※ 참고 블로그
[C#][Unity] is as 캐스팅 연산자
is, as는 C#의 캐스팅 연산자로 객체를 캐스팅 할때 사용. 기본적으로 상속관계의 클래스간 하향캐스팅을 할 때 사용된다. 하향캐스팅은 명시적으로 이루어져야 하는데 실행시점에 실패 할 가능
zagara.tistory.com
>> WalkState.cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.InputSystem;
public class WalkState : MonoBehaviour, IState
{
public StateMachine Fsm { get; set; }
public Blackboard_Default Blackboard { get; set; }
public void InitState(IBlackboardBase blackboard)
{
Blackboard = blackboard as Blackboard_Default;
}
public void Enter()
{
Blackboard.animator.CrossFade("Idles", 0.1f);
Blackboard.animator.SetFloat("Speed", 1.0f);
}
public void UpdateState(float deltaTime)
{
if (Blackboard.jumpInput.triggered && Blackboard.rigidbody.velocity.y == 0.0f)
{
Fsm.ChangeState<JumpState>();
return;
}
var value = Blackboard.moveInput.ReadValue<Vector2>();
if (0 >= value.sqrMagnitude)
{
Fsm.ChangeState<IdleState>();
return;
}
Blackboard.rigidbody.velocity = new Vector3(value.x * Blackboard.moveSpeed, Blackboard.rigidbody.velocity.y, value.y * Blackboard.moveSpeed);
}
public void Exit()
{
}
}
>> JumpState.cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class JumpState : MonoBehaviour, IState
{
public StateMachine Fsm { get; set; }
public Blackboard_Default Blackboard { get; set; }
public void InitState(IBlackboardBase blackboard)
{
Blackboard = blackboard as Blackboard_Default;
}
public void Enter()
{
Blackboard.animator.CrossFade("Jump", 0.1f);
Blackboard.rigidbody.velocity = new Vector3(Blackboard.rigidbody.velocity.x, Blackboard.jumpForce, Blackboard.rigidbody.velocity.z);
}
public void UpdateState(float deltaTime)
{
if (Blackboard.rigidbody.velocity.y == 0.0f)
{
Fsm.ChangeState<IdleState>();
}
}
public void Exit()
{
}
}
└ Factory Pattern + Extention Method (확장 메서드) + Collection
>> StateMachine.cs
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Unity.VisualScripting;
using UnityEngine;
public enum StaterType
{
None,
Character,
Max
}
// 확장 메서드 (this StateMachine) + 팩토리 메서드 패턴 + 컬렉션 (List)
public static class StateFactory
{
public static List<IState> CreateStates(this StateMachine stateMachine, StaterType staterType)
{
List<IState> stateList = new List<IState>();
switch (staterType)
{
case StaterType.Character:
{
stateList.Add(stateMachine.AddComponent<IdleState>());
stateList.Add(stateMachine.AddComponent<WalkState>());
stateList.Add(stateMachine.AddComponent<JumpState>());
}
break;
}
return stateList;
}
}
public class StateMachine : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField]private string defaultState;
private IState currentState;
private Dictionary<Type, IState> stateDict = new();
public void Run()
{
IBlackboardBase blackboardBase = GetComponent<IBlackboardBase>();
blackboardBase.InitBlackboard();
List<IState> states = this.CreateStates(StaterType.Character); // this == StateMachine instance
foreach (var state in states)
{
AddState(state, blackboardBase);
}
ChangeState(Type.GetType(defaultState));
}
public void AddState(IState state, IBlackboardBase blackboard)
{
state.Fsm = this;
state.InitState(blackboard);
stateDict.Add(state.GetType(), state);
}
public void ChangeState<T>() where T : IState
{
ChangeState(typeof(T));
}
public void ChangeState(Type stateType)
{
currentState?.Exit();
if (!stateDict.TryGetValue(stateType, out currentState)) return;
currentState?.Enter();
}
public void UpdateState()
{
if (currentState != null)
currentState.UpdateState(Time.deltaTime);
}
}
Expention Method (확장 메서드)
: 기존 형식에 Method를 추가할 수 있다.
>> 사용법
- static class로 만든 후, 확장 메서드로 사용할 static 메서드를 만든다.
- 확장하려는 클래스를 매개변수의 첫 번째로 두고, 앞에 키워드 this를 붙인다.
- 확장하려는 클래스의 인스턴스 뒤에 dot을 찍고 확장 메서드를 사용한다.
public static List<IState> CreateStates(this StateMachine stateMachine, StaterType staterType)※ this StateMachine stateMachine : StateMachine가 실행 주체라는 의미 --> 나의 this는 StateMachine이라고 공표
※ StateMachine에 CreateStates 함수를 주입한다는 의미
Factory Pattern
: 각 State 별로 함수를 따로 정의해주는 것
※ 사실 잘 안 쓰는 방식인데, 배워보는 것
※ 참고 블로그
https://glikmakesworld.tistory.com/5
유니티 디자인패턴 - 팩토리(심플팩토리, 팩토리 메소드, 추상팩토리) (Unity Design Patterns - Factory)
흔한 프로그래밍 언어서 새로운 인스턴스를 만들 때 new를 사용한다. 만약 내 게임의 스테이지1에서 그린고블린을 만든다면 아래와 같이 만들것이다. GreenGoblin greenGoblin = new GreenGoblin(); 만약 유니
glikmakesworld.tistory.com
Collection
List<T> : C#의 동적 Generic Collection Class
※ 생성한 'stateList'는 IState를 구현한 상태 객체(IdleState, WalkState, JumpState)를 저장한다.
이후, MyChan에 넣어둔 State Script들을 제거
: Factory를 통해 State들을 만들어줬기 때문

'Development > Unity BootCamp' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 멋쟁이사자처럼부트캠프 Unity 게임 개발 3기 32~37일차 (0) | 2025.01.15 |
|---|---|
| 멋쟁이사자처럼부트캠프 Unity 게임 개발 3기 31일차 (1) | 2025.01.13 |
| 멋쟁이사자처럼부트캠프 Unity 게임 개발 3기 27일차 (0) | 2024.12.27 |
| 멋쟁이사자처럼부트캠프 Unity 게임 개발 3기 26일차 (0) | 2024.12.26 |
| [멋쟁이사자처럼 부트캠프 TIL 회고] Unity 게임 개발 3기 18일차 (0) | 2024.12.19 |



